What Every Woman Should Know About Free Radical Damage
Many of us have heard buzzwords like "free radicals" and "antioxidants," but it can be tricky to get the facts straight. For one, it seems like advertisers for every product, from food to makeup try to highlight the fact that their products contain antioxidants. However, they don't explain how or why that is beneficial to our health.
Advertisers like to tout the benefits of antioxidants because they protect the body from free radicals. Free radical damage occurs in the body as we age, but certain foods and lifestyle factors can speed up this process, causing more damage. But what does all this even mean? Here, we'll explore why free radicals are so harmful and what to do about it.
What are free radicals?
Free radicals are atoms that contain an odd number of electrons. These free radicals can exist inside or outside our bodies. Atoms should have an even number of electrons to be stable, so when they lose one, they can become unpredictable. Because of this odd number, free radicals are unstable and can easily cause our cells to change quickly.
Our bodies need some free radicals to function, but too many leads to chemical changes. Free radicals are highly reactive, meaning they can easily cause changes in the body. Too many free radicals is dangerous, because they cause damaging chemical reactions in the body. They are able to make significant changes to our DNA and the makeup of our cells. This causes our cells to die or mutate, which leads to serious diseases, such as cancer.
Our bodies produce free radicals naturally, but we can also take them in from our food or even the air we breathe. Free radicals are created during a process call oxidation.
What is oxidation?
Oxidation occurs in our bodies everyday. Oxidation just refers to the process of our cells coming in contact with oxygen. Just like oxygen can cause rust on an old bike, it causes changes in our bodies. However, there are certain lifestyle factors that can speed up oxidation. When we expose our bodies to dangers like cigarette smoke or stress, oxidation occurs faster. When this happens, free radicals are created and start the process of changing our cells.
The bummer is that so many delicious treats (like fried foods and alcohol) lead to our bodies producing too many free radicals. Free radicals are even produced when we exercise, because as we breathe harder and faster, our bodies take in more oxygen. This leads to oxidation and the production of free radicals. While too much exercise can certainly lead to injury, going for a jog or to yoga class is, of course, not going to cause damage. The problem comes when oxidation is occurring too fast, and our bodies can't compensate for all the changes. Too much oxidation leads to oxidative stress.
What is oxidative stress?
While oxidation is a normal body process, oxidative stress is not. Oxidative stress occurs when oxidation is sped up too much by external factors, like smoking or tanning. Once our bodies cannot keep up with protecting us against these free radicals, our cells change and are at risk for mutating and causing diseases. So one glass of wine at the office happy hour is fine, but if it leads to ordering more drinks and nachos for the table, your body is going to have a hard time protecting your cells.
We also know that oxidative stress leads to inflammation in the body. This inflammation can then lead to a ridiculous number of chronic conditions like arthritis, heart disease, stroke, cancer, and even Alzheimer's disease. In order to protect our cells against this damage, our bodies need antioxidants to stop the free radicals from being produced and wreaking havoc on our cells.
What are antioxidants?
Antioxidants help to fight and protect against this oxidation process. Antioxidants are able to safely interact with free radicals and stop their damage. Think of free radicals like an overtired toddler who just ate a few cupcakes. He might be fine, but you just don't know. He is highly volatile and might even throw a tantrum. Well, if free radicals are the toddler, antioxidants are the soothing mom singing his favorite song. Antioxidants can calm down and neutralize free radicals, keeping them from being harmful to others.
Our body produces antioxidants, but we can also get them from eating foods with certain vitamins and minerals. Our bodies need the right balance of free radicals and antioxidants to function properly and repair cell damage everyday.
Antioxidants may protect us from many chronic diseases such as cancer and heart disease. A study from the American Medical Association concluded that adding antioxidant-rich foods to our diets is protective against cognitive decline as we age. So if you'd like to stay sharp in your 90s, start loading up on the antioxidants now.
Antioxidants are found almost exclusively in plant-based foods, so put down that steak and grab a salad.
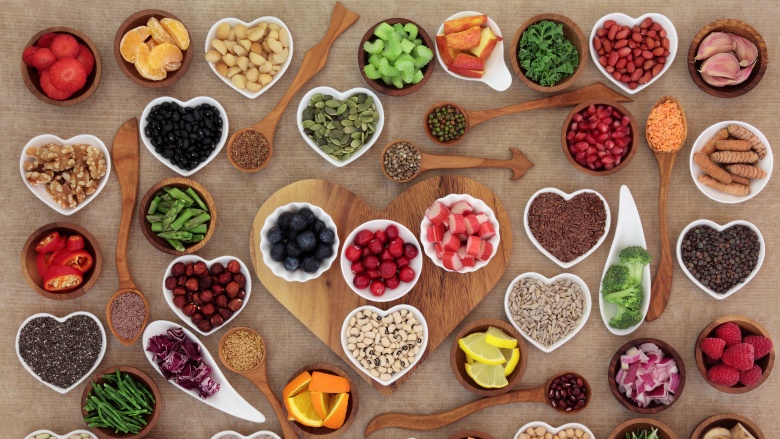
Antioxidant foods
The best way to judge if a plant food is rich in antioxidants is to look at its color. Antioxidants are found in fruits and vegetables with deep, rich colors. Iceberg lettuce isn't going to cut it. Antioxidant foods are also usually high in fiber and essential vitamins.
The antioxidant beta carotene found in vitamin A causes an orangish color and can be found in sweet potatoes, carrots, orange bell peppers, and cantaloupe. Beta carotene improves our immune systems and is even protective against cancer and aging. Oranges are also high in beta carotene, along with vitamin C.
Anthocyanins are powerful antioxidants that give foods a deep red or blue color. Think beets, kidney beans or berries. These little powerhouses can improve heart health and even memory. They are also linked to preventing some types of cancer.
Flavonoids are antioxidants that boost brain function and improve inflammation. They are found in tons of fruits like berries, pears, apples, and apricots. They are also found in tea, soy, and black beans. Oh and here's something to get your attention. Wine and cocoa are both rich in flavonoids. Wine Wednesday with some chocolate for better brain health? Cheers to that!
Isothiocyanates are antioxidants found in broccoli, kale, and cauliflower. They help the body with the detoxifying process and even protect against breast and prostate cancers. When it comes to greens like spinach or kale, go for the darkest varieties for the most nutrients.
The more, the better
Research has shown that no one single antioxidant can protect us from disease. They have to work together. That is why it's so important for all of us to eat a variety of fruits and vegetables each and every day. Your mom was right when she told you to eat the rainbow. Generally speaking, the more (natural) colored foods on your plate, the better!
Antioxidants not only stop free radical damage, they can actually prevent these dangerous free radicals from even occurring.
Skip the supplements
Once research studies started showing the benefits of antioxidants, every food company started adding them to their packaged food products. We don't know if antioxidant supplements have the same protective qualities, so it's best to stick with fresh fruits and vegetables. Some studies have looked at the effects of supplements, and the results are mixed.
Antioxidant supplements may even do more harm than good. One study found that taking a vitamin E supplement everyday actually increased the risk of prostate cancer in the men studied. Taking antioxidant supplements has also been linked to increased skin cancer risk in women.
Taking an antioxidant supplement as part of your treatment if you already have cancer is probably not a good idea either. They have not been proven to be helpful, and could even make things worse, especially if you're a smoker.
Both the American Heart Association and the American Cancer Society recommend eating antioxidants from food rather than supplements. Because these antioxidant supplements are not regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the manufacturers can claim all kinds of health benefits without having to prove them. To be safe, stick with rich, colorful produce for your antioxidant fix. Look for deep reds like pomegranates, oranges like sweet potatoes and greens like spinach. Eating a diet rich in fruits and vegetables can protect against free radicals, so go natural.