When You Take Melatonin Every Night, This Is What Happens To Your Body
Think of melatonin as the sandman hormone — it helps to regulate your body's internal clock and its rhythm of sleeping and waking, as explained by Medical News Today. Melatonin as an oral supplement can also help encourage this cycle; it has been proven to effectively reduce the average amount of time it takes someone to fall asleep and encourage a more restful state of slumber (via Neurological Research). What's more, it has some additional effects beyond its bedtime benefits.
A powerful antioxidant, melatonin can maintain eye health, foster the production of human growth hormone, and maybe even ward off some forms of depression, according to Healthline. Moreover, since it is considered safe, it can be a great alternative treatment or preventative measure for certain ailments, as noted by the publication.
Want to know if you should add melatonin to the mix and start taking this seemingly magical pill daily? You snooze, you lose — so learn the facts. This is what happens to your body when you take melatonin every night.
You may fall asleep more readily if you take melatonin every night
You turn off electronics well before bedtime, dim the lights, and do some meditative breathing exercises — and yet, you still end up staring at the ceiling for an hour or two before finally dozing off to sleep at night. If falling asleep (without having to count a million sheep) is your problem, choosing to take melatonin every night could be the solution.
A study in the Journal of Sleep Research sought to prove that melatonin can reduce your core temperature, consequently setting you up for a more successful sleep onset latency (or the amount of time it takes to nod off).
Researchers gave either melatonin or a placebo to adults at 2 p.m., and monitored changes in their core temperature through the afternoon and evening hours. The findings confirmed their hypothesis; those who were given the melatonin during the day had a lowered core temperature an hour and a half later and it sustained for six hours. Those in the experimental group also had a decreased onset latency. In other words, they fell asleep quicker than those who were given the placebo.
If you want to do more than take melatonin every night to fall asleep faster, take note of things you should never do right before bed, including eating certain foods.
If you take melatonin every night, you could help quell insomnia and other sleep disorders
If you are one of of the 70 million Americans affected by a sleep disorder (via Cleveland Clinic), you may feel desperate in what seems like a never-ending quest for quality Z's.
Varying degrees of sleep disorders can affect your potential to snooze soundly on a night-to-night basis, and can lead to several minor and major consequences. Over time, sleep deprivation could inhibit your ability to function, work, or drive, as noted by Healthline. It also puts you at a higher risk for other serious medical conditions.
While there are several insomnia medications on the market, many are linked to "dependence and addiction," as per an analysis in Neurological Research, which noted, "Moreover, some of these medications can gradually impair cognition." Melatonin, on the other hand, has no reported side effects. It works to "synchronize the circadian rhythms," ultimately helping the "duration and quality of sleep." The report found that it "is effective for ameliorating" several common sleep disorders, including insomnia, some cases of obstructive sleep apnea, and potentially even hypersomnolence (i.e. narcolepsy). So, it may be a good idea for you to take melatonin every night.
You can help you combat a rough case of jet lag if you take melatonin
Ever hear someone say they need a vacation from their vacation? Traveling is great and all, but the lingering effects of jet lag can suck some of the joy out of taking a trip and make returning to a routine back at home a totally exhausting feat.
Fortunately, melatonin can help you adjust. As noted by a study in Current Treatment Options in Neurology, if you are traveling east, you should consider reseting your internal clock by "advancing sleep and wake times and circadian timing ... with evening melatonin and morning bright light" a few days before leaving for your trip. While this can help you avoid jet lag altogether, it may not be possible for some people. You can try an alternative option that can help you curb the effects of jet lag upon arrival at your travel designation — avoid "early morning light and exposure to late-morning and afternoon light," and take melatonin right before bed. Conversely, if you are traveling west, you can alter your circadian cycle upon arriving with "afternoon and early-evening light" and a dose of evening melatonin.
Similar principles can be applied to those who regularly work the nightshift and need to alter their circadian rhythm to keep alert on the job and get rest during off hours.
You may reduce symptoms of heartburn and acid reflux when you take melatonin every night
Those who regularly suffer from acid reflux or GERD know that the painful burn can last all day and night. While there are plenty of over-the-counter and prescription antacid drugs available, melatonin may be a more natural alternative.
Previous evidence has shown that melatonin might be able to "protect the gastrointestinal mucosa from oxidative damage;" so researchers set out to see if it could be used as an effective treatment. The study, published in BMC Gastroenterology, involved 36 participants with acid reflux who were split into four groups. For weeks, one group was given melatonin, another was administered omeprazole ("a proton pump inhibitor") alone, and a third group was prescribed a combination of melatonin and omeprazole. The fourth group was a control.
The results indicated that melatonin can be a useful part of a reflux treatment plan. It's effective when used alone or in tandem with omeprazole. However, the use of just omeprazole is better than melatonin alone. So, if you suffer from acid reflux, you might want to start to take melatonin every night. And you'll probably want to avoid the worst foods for acid reflux, too.
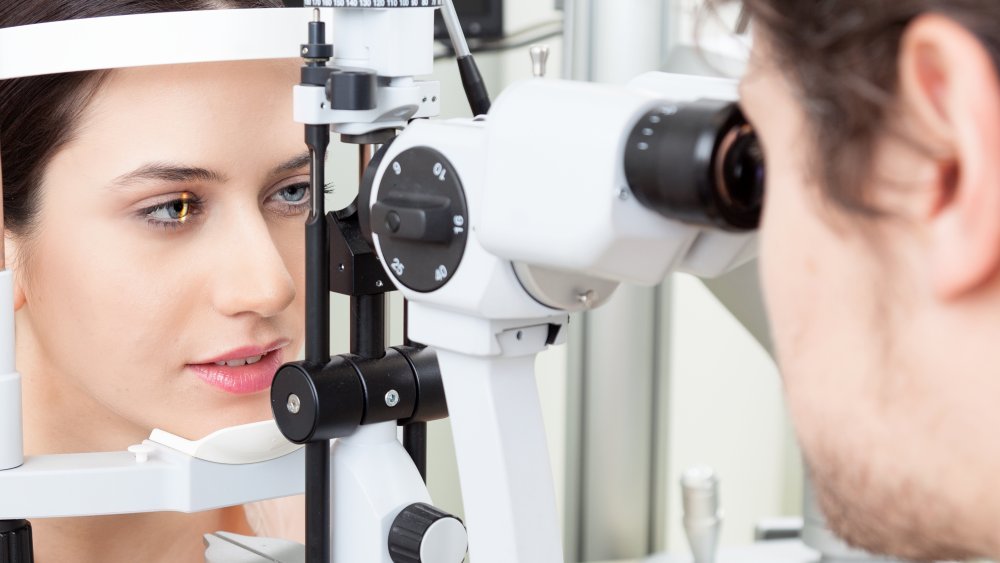
If you take melatonin every night, you could reduce your risk of macular degeneration and other eye diseases
When you take melatonin every night, it may help regulate your sleep and wake cycles, but it could potentially also treat degenerative eye diseases — and even prevent blindness.
According to Science Daily, a model study published in the American Journal of Pathology found that melatonin could reduce ocular inflammation of two key receptors in people with uveitis, a serious eye disease that causes pain, redness, swelling, and even blindness in 10 to 15 percent of patients. Furthermore, melatonin was also shown to reduce the occurrence of "clinical symptoms of uveitis such as inflammation, blood vessel expansion and cataract." It even was able to protect the blood-ocular barrier. Since melatonin does not have any dangerous "collateral effects," head researcher Dr. Ruth Rosenstein of The University of Buenos Aires believes that melatonin could be a "promising" treatment either alone or in tandem with other therapies for patients with uveitis.
Another study in Visual Neuroscience showed preliminary evidence that melatonin may also be useful in the treatment of other eye diseases such as glaucoma and age-related macular degeneration.
If you take melatonin every night, will it play a role in seasonal affective disorder?
As explained by Dr. Norman Rosenthal, professor of psychiatry at Georgetown University Medical School, in Psychiatry (Edgmont), seasonal affective disorder (SAD) is a specific type of depressive disorder marked by its occurrence "during the short, dark days of winter."
As a naturally occurring hormone, melatonin plays a major role in the onset of this temporary mental condition. As indicated by the Journal of Neural Transmission, previous research showed that "bright environmental light" can reduce your body's natural production of melatonin, subsequently diminishing the symptoms of seasonal affective disorder.
In a study performed by Oregon Health And Science University, 68 participants with seasonal affective disorder were assigned to one of three separate groups, and respectively given a placebo, melatonin early in the day, or melatonin in the afternoon hours (via Science Daily). The researchers realized that those individuals with SAD who had a tendency to stay up late at night benefited from afternoon or evening melatonin, whereas early birds responded well to morning melatonin.
Wondering if you're suffering from SAD? Here are four signs you may have seasonal affective disorder. Be sure to share your concerns with your doctor.
You may feel tired during the day if you take melatonin every night
You want to feel fresh, invigorated, and well rested after a full night of melatonin-induced sleep. But could taking the supplement leave you feeling groggy and slow?
According to Healthline, taking melatonin during the day may not be advisable as it can cause grogginess outside of the usual bedtime hours. What's more, daytime sleepiness could be a potential side effect in those who take a longer amount of time to clear the drug from their systems. "Reduced melatonin clearance" is common among "older adults and infants."
Still, it seems that most people won't encounter daytime exhaustion as a result of taking melatonin. In a study published in the Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, individuals were intravenously given either 10 mg of melatonin, 100 mg of the supplement, or a placebo. Interestingly, none of these participants reported any effects on their ability to stay awake and focused.
Men could experience an increase of human growth hormone if they take melatonin every night
According to WebMD, human growth hormone (HGH) is made by the pituitary gland. It fosters healthy development and growth in kids and adults alike. Synthetic HGH is used to bolster growth in children who have not thrived on their own. There are other specific uses for adults too, such as short bowel syndrome. What's more, many people seek to use it to bulk up — despite the fact that this use is not approved by the FDA (via WebMD).
But there might be a simpler way to boost your body's natural production of HGH. A study in Clinical Endocrinology noted that taking melatonin bolstered human growth hormone in those who took it orally.
As noted by Healthline, melatonin, generally speaking, has no real dangerous side effects — so it could be a good therapy for those looking for more natural means. Per the health site, "To maximize its effects, take 1–5 mg about 30 minutes before bed. Start with a lower dose to assess your tolerance, then increase if needed." Furthermore, as explained by Healthline, getting good sleep also boosts levels of growth hormone — so the effects of melatonin could be twofold.
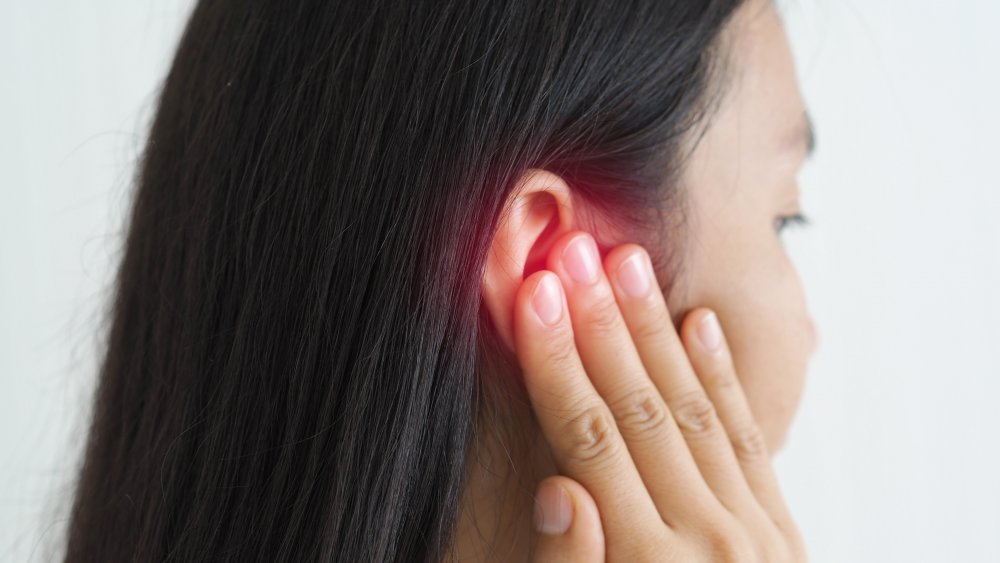
If you take melatonin every night, it could help relieve ear ringing
If you suffer from regular tinnitus, you will likely do just about anything to stop that nagging, high-pitched ringing in your ears. Fortunately, you might be able to take melatonin every night and put an end to the tenacious tone.
A study published by The Annals of Otology, Rhinology, and Laryngology assigned participants who reported experiencing frequent tinnitus to one of two groups; they either received 3 mg of melatonin or were given a placebo each night for a month. The results confirmed that melatonin can cause a reduction in the "intensity" of tinnitus. Furthermore, those who took melatonin slept better despite their tinnitus.
The research also noted that melatonin is significantly more effective in males who do not or have not previously suffered from depression and those who have not tried seeking other avenues of treatment for their tinnitus.
When you take melatonin every night, it could help ease your anxiety
If melatonin mellows you out for bed, can it also ease everyday anxiety? As noted by Healthline, a majority of research around melatonin's effect on anxiety revolves around its pre- and post-operative uses versus everyday generalized anxiety. Still, a look at its acute effect on reducing anxiety can lay the foundation for its potential use as a mental health treatment.
An analysis of eight studies helped researchers conclude that, compared to a placebo, taking melatonin before a procedure can significantly decrease a patient's anxiety. In fact, it can be just as useful as an anti-anxiety medication like midazolam (via Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews). A 2018 study in Annals of Pharmacotherapy determined that melatonin was even more effective than traditional treatment, oxazepam, in reducing anxiety in patents who had just had heart surgery. Finally, one promising study in Aging Clinical and Experimental Research found that melatonin was more effective than a placebo at treating older adults with behavioral disorders, and helped relieve depression and anxiety. Some participants were even able to trade in their regular prescriptions for melatonin supplements.
The anxiety-fighting potential of melatonin seems encouraging, but more research is still needed.
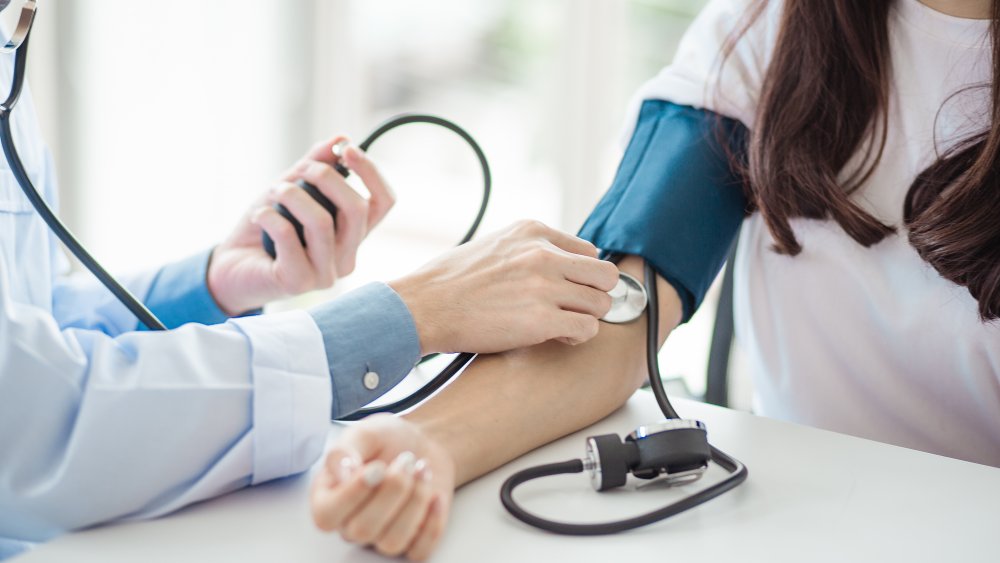
You could lower your blood pressure if you take melatonin every night
Research is still in its infancy, but many scientists have come to believe that melatonin supplements may be an effective alternative in the treatment of hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases.
As noted by an article in Cardiovascular Endocrinology and Metabolism, blood pressure has a circadian rhythm — it increases when you wake and subsequently leads to high numbers throughout the day, followed by a big drop in the evening hours.
Since melatonin is a circadian hormone, it might have a reductive effect on blood pressure. As melatonin has antioxidant power, it can decrease catecholamines, hormones released by the adrenal glands during moments of distress (Verywell Mind), and force the dilation of blood vessels by fostering the body's ability to make nitric oxide. This all reportedly translates to lower blood pressure. As noted by the analysis, additional research is needed to solidify melatonin's promising position as a potential blood pressure treatment.
Can taking melatonin every night help with ADHD?
It is common that those who are diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder may find themselves experiencing common sleep impairments. One study published in Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment set out to demonstrate melatonin's effectiveness in helping children with ADHD and treating their respective sleep issues.
Of 74 youngsters given melatonin, 45 of them — a significant 60.8 percent — responded well to the circadian supplement. Effectiveness did not vary based on mood disorders, learning disabilities, or "disruptive behavior disorders," such as "oppositional defiant disorder or conduct disorder."
This is good news, of course, for those kids with ADHD — and their parents — whose lives are affected by sleep deprivation. However, as explained by WebMD, while it seems that melatonin can help with the sleep disorders that often go hand in hand with ADHD, the supplement does not actually serve to treat ADHD or help to reduce its symptoms.
When you take melatonin every night, it might help with hair loss and dandruff
While a little bit of hair loss is totally normal, people who see a significant amount of shedding can feel alarmed and dismayed. Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease that causes the body to attack its own hair follicles, leading to excessive hair loss and potential balding (via WebMD).
While there are some treatments available on the market, a more natural alternative might be available — and preferable. And it might even benefit those who have not been diagnosed with a form of alopecia, but still want to reduce thinning. An analysis of five clinical studies in the International Journal of Trichology indicated that the use of topical melatonin in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia could be effective. Thirty participants in an observational study reported a major decrease in the "severity of alopecia after 30 and 90 days." Another study cited indicated that it might be more helpful in women than men.
An added bonus? Participants saw a reduction in scalp dandruff, too.
When you take melatonin every night, it could help your skin look younger and more revitalized
When you take melatonin every night, it might provide more than beauty sleep, as it could actually have aesthetic benefits. As a powerful antioxidant, melatonin's abilities may be useful in treating and protecting your skin and fighting the effects of environmental pollution and stress, according to Elle. As noted by the magazine, melatonin often works with anti-aging ingredients such as retinol and brightening agents like vitamin C; and, while many women use products containing the antioxidant in their evening routine, doctors are also urging patients to try applying a topical product with melatonin during the day. The ingredient could also keep you safe from the harmful effects of UV rays.
"Think of it as a potential new sun protection ingredient," New York City-based dermatologist Ellen Marmur told Allure. "Topical melatonin theoretically might help to intercept UV photons."
Another reason melatonin is a great skincare ingredient? It's relatively safe. A study in the Journal of Dermatological Treatment looked at the consequences of applying topical melatonin to 80 percent of the body and found no link to cognitive issues or underlying effects.