When You Go Tanning Every Day, This Is What Happens To Your Body
If you're a person who goes tanning every day, you know there's an endless amount of options when it comes to achieving sun-kissed skin. You can tan in your own backyard, at the tanning salon, while vacationing on some beautiful, unusual island, or even by getting your first spray tan. But what's happening to your body every time you frequent a tanning bed or lay under the hot sun for hours at a time? Well, according to the FDA, you're damaging your body's largest organ: your skin.
"The body does not create a tan to be pretty — there is no evolutionary advantage of that," Mayo Clinic dermatologist Aleksandar Sekulic told Self. "Rather, tanning is a direct response to the mutations that occur in our DNA." In other words, simply exposing yourself to the sun's rays is damaging your body's cells and placing you at a higher risk for developing skin cancer.
So, what concerns should you have if you expose your body to UV light on a daily basis? Keep reading to discover just what happens to your body when you go tanning every day. Warning: the results aren't so sunny.
When you tan every day, your skin cells are being damaged
Tanning every day may appear harmless, but, in reality, lying out in the sun is actually damaging your skin's DNA.
According to Dr. Doris Day, a cosmetic dermatologist, the sun emits two types of ultraviolet rays — shortwave (UVB) and longwave (UVA). As Dr. Day explained to Cosmopolitan, UVB rays penetrate your epidermis, the skin's outermost layer. And while the cells in your epidermis regenerate every 28 days — when you go out in the sun without protection, UVB rays can cause serious DNA damage to your skin.
As it turns out, a nice tan is a double-edged sword. "What the cells do with this pigment they received as a gift is pile it all on top of the cell's nucleus, like an umbrella," Dr. Aleksandar Sekulic told Self. According to the doctor, this causes your skin goes into recovery mode, triggering melanocyte cells to increase melanin production, which subsequently results in a darker complexion. As Day told Cosmopolitan, the body is simply trying to protect itself from serious, long-lasting sun damage; however, its form of self defense just so happens to appear as a much-desired tan.
When you tan every day, your chance of skin cancer increases
Unfortunately, when you tan every day, you greatly increase your chances of developing skin cancer.
As reported by the American Cancer Society, your skin tans as it absorbs the sun's ultraviolet rays, and those rays cause an increase in melanin-producing melanocyte cells. While melanin blocks some of the dangerous UV rays, light-skinned people — who have significantly less melanin — are far more likely to burn than their darker-skinned counterparts. However, as Dr. Michael Lin told Healthline — even if you're blessed with an abundance of melanin, UV exposure can still raise your chances of developing skin cancer. "Darker-skinned people can still develop skin cancer and experience photoaging, [which is] premature aging of the skin caused by repeated sun exposure," Lin revealed.
According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, the truth about tanning and skin cancer is that indoor tanning beds can be even worse for your skin. The foundation reported that a person is 75 percent more likely to develop "life-threatening melanoma from just one indoor tanning session" before their 35th birthday. Yikes!
Tanning every day can cause premature aging
If you tan every day, you probably don't want to hear that too much tanning may result in unwanted wrinkles. However, the FDA warns that basking in the sun for too long will likely cause premature aging — or photoaging — much earlier than you'd like.
So, what does this warning mean for your skin? Well, if you rely on false facts you believe about sunscreen and skip the SPF, your skin will undoubtedly age faster due to the sun's strong UV rays. As the FDA notes on its website, this "unprotected exposure to harmful UV rays breaks down the collagen and elastin fibers in healthy young skin, and causes wrinkles and loosened folds."
While there isn't a way to avoid aging skin, the Canadian Dermatology Association reports that — unlike natural, chronologic aging — skin exposed regularly to UV rays can appear a different color, texture, and may even include dark spots. According to the Canadian Dermatology Association, the photoaging process can reportedly begin as early as one's teen years or early 20s; however, your risk is determined by your skin type and the amount of unprotected sun exposure your skin receives.
If you tan every day, it could cause eye damage
If you go tanning every day, you should make it a point to use protective eyewear.
As the FDA reports, high amounts of UV exposure can cause eye cataracts, which could result in vision impairment and even blindness. Other forms of eye damage include macular degeneration, atypical tissue growth, and photokeratitis — which is essentially a sunburn of the cornea. And while you may assume tanning beds are safer for your eyes than the sun's rays, that's simply not true. "Tanning beds can produce UV levels up to 100 times what you would get from the sun, which can cause serious damage to the external and internal structures of the eye and eyelids," the American Academy of Ophthalmology notes on its website.
"UV damage is cumulative. That's why teens and young adults should be particularly careful to protect their eyes from sun exposure," ophthalmologist Philip R. Rizzuto told The American Academy of Ophthalmology. According to the FDA, the best way to avoid eye damage is to wear a hat and 100 percent UV protection sunglasses while tanning outdoors, and protective goggles when tanning indoors. Your eyes will thank you!
You don't need to tan every day to get your necessary vitamin D dosage
While you might go tanning every day under the assumption that your body is soaking up a healthy amount of vitamin D in the sun, Dr. Madeliene Gainers of Anne Arundel Dermatology told Healthline that there's no reason to tan for extended periods of time to achieve high vitamin D levels.
"There's no reason to damage the skin, putting oneself at risk for skin cancer as well as accelerated aging, to get vitamin D," Gainers said. Of course, your body does need vitamin D; however, there are healthier ways to get your fill — including implementing a vitamin D rich diet and taking daily supplements.
Interestingly, as reported in Science Daily, your tanned skin may actually be blocking "vitamin D synthesis," limiting your body's ability to produce vitamin D at all. Fortunately, according to the World Health Organization, five to 15 minutes of sun two to three times a week during the summertime is all you need to help your body produce healthy vitamin D levels. In other words, there's no need to spend the whole day tanning just to soak up some vitamin D.
Tanning every day can become an addiction
If you go tanning every day, you might have an actual addiction to the act of tanning.
In a 2017 study conducted by Georgetown University Medical Center, a little more than 20 percent of women tested showed what researchers referred to as "signs of tanning dependency" where indoor tanning was concerned. According to Skin Cancer Foundation president Deborah S. Sarnoff, the first step in helping people break this dependency is figuring out why they want to tan so often in the first place. "Understanding why people feel compelled to tan is important, because it helps physicians and other health care advocates develop better intervention techniques that encourage people to stop tanning," Sarnoff said (via the Skin Cancer Foundation's Sun & Skin News).
As reported in the 2017 study, women who showed a dependency reportedly believed tanning helped lift their moods, while also making them feel better about their appearances. Still, Sarnoff said she'd like to make tanning salons illegal. "There is no such thing as a healthy UV tan," Sarnoff said. She continued, explaining, "Whether you're laying out on the beach or in a tanning bed, the damage your skin sustains can lead to skin aging and potentially deadly skin cancer."
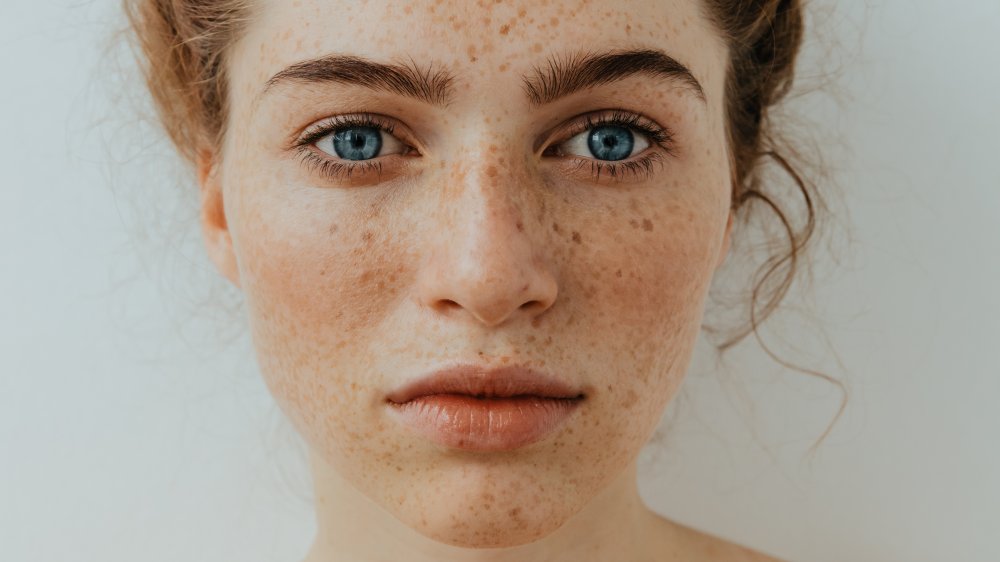
You might have more freckles if you tan every day
If you tan every day, new freckles may start making a home on your face. And while they may look cute, freckles that suddenly appear or darken after sun bathing could be a sign of sun damage, dermatologist Keira Barr told Byrdie.
"The appearance of freckles, technically called ephelides, is a tell-tale sign of excessive sun exposure on unprotected skin," Barr told Byrdie. According to the dermatologist, these freckles are typically seen in areas often exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, and arms. However, there's no need to panic if you happen to have freckles in these places. As Dr. Joshua Zeichner told Byrdie, freckles aren't necessarily cause for concern, unlike certain moles and sun spots, "Under the microscope, freckles have a normal number of pigment-producing cells that produce extra amounts of pigment," Zeichner explained.
Still, Barr recommends visiting your dermatologist regularly, as freckles could be indicators of UV damage — and perhaps an increased risk of skin cancer. "Individuals with a high density of freckles were found to have a greater risk for developing melanoma than those without freckles," Barr told Byrdie.
Tanning every day could zap acne... but the risk is greater than the reward
Tanning every day may seem to help zap pesky zits, but you shouldn't skip the sunscreen and head outside for a sunny DIY facial. As dermatologist Ava Shamban told InStyle, while UV rays may seem to clear some acne breakouts, the rays do more harm than good for your skin. "UV rays are lethal to P. Acnes, the main bacteria that contributes to acne, but they also injure the skin, causing brown spots, wrinkles, and sagging," Shamban explained.
Sometimes, a tan may give the desired appearance of clearer skin — however, the reality could be that your darker skin is actually just camouflaging your breakouts and blemishes. "The problem with [the tanning] approach is that once the tan fades, the skin is left looking more discolored than before," Dr. Elizabeth Tanzi told InStyle.
According to Dr. Doris Day, the sun could actually dry out your skin and create more oil, leading to even more zits (via Cosmopolitan). So, it's probably just better to stay on the safe and sunless side and skip out on sun bathing if you're chasing after a clear complexion.
When you tan every day, stretch marks become more noticeable
Unfortunately, tanning every day won't make your stretch marks from pregnancy or other types of weight gain disappear. In fact, constant tanning could have quite the opposite effect on those stretch marks you're looking to get rid of for good.
According to the American Academy of Dermatology Association, tanning too often will actually make the unwanted marks more visible, as stretch marks don't tan. If you're seeking to hide those pesky stretch marks, the association recommends using self-tanners, as these products will actually work to hide the scars temporarily.
So, why doesn't the sun have the same effect on stretch marks as it does on the rest of your skin? Well, according to Everyday Health, stretch marks are essentially scar tissue — meaning they don't respond to the sun like other areas of your skin do. "Scars don't have functional melanocytes to the same extent as non-scarred skin," Dr. Harold Lancer told StyleCaster. He continued, explaining, "Stretch-mark-damaged skin has an unreliable skin-repair mechanism, so chances are they will not tan to the same color as the rest of the skin."
You might fall victim to dandruff if you tan every day
If you spend hours tanning every day in the sun, you're probably well-acquainted with a little something called dandruff. However, if you're seeing those pesky white flakes often, perhaps you should consider them a sign that you're getting too much sun.
Just as too much tanning stresses out your skin, the sun can also negatively impact your scalp. According to Head & Shoulders, humidity is not your scalp's friend. And, if you frequent tanning beds or spend days getting hot and sweaty on the beach, you're likely causing your scalp to develop a moist environment in which dandruff will undoubtedly thrive (and annoy you to no end with its itchy flakes).
Of course, sunburn is an ever-present risk for frequent tanners. According to Van Scoy Hair Clinics, even if you have a healthy head of hair, your scalp can get sunburned, too — possibly causing major damage to your hair follicles. As noted by Healthline, massaging sunscreen into your scalp prior to sun exposure is a good sun-safety habit to develop, as is wearing a protective hat or cap to avoid unnecessary sun damage to your sensitive scalp.
On a positive note, tanning every day could lift your spirits
If tanning every day under the hot sun makes you feel better, you're not alone. According to Time, studies have linked high levels of serotonin (a feel-good chemical) with an abundance of sun exposure. There's even research to suggest that UV light from tanning beds may "trigger feelings of euphoria," while also prompting the melanocytes that produce the dark pigment on your skin "to release endorphins."
According to Science Daily, a study done by Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center concluded that frequent tanners reportedly experienced psychological benefits from tanning. "A more relaxed and less tense mood was reported after UV exposure compared to after non-UV exposure," lead researcher Steven Feldman told Science Daily. He continued, saying, "We believe these relaxing and reinforcing effects contribute to tanning behavior and may help explain why people choose to tan despite the risks."
Unfortunately, endorphins can't be accurately measured; however, Feldman noted that the study's findings "suggest a course for future research into why people use tanning beds and the mechanism of mood changes associated with tanning."
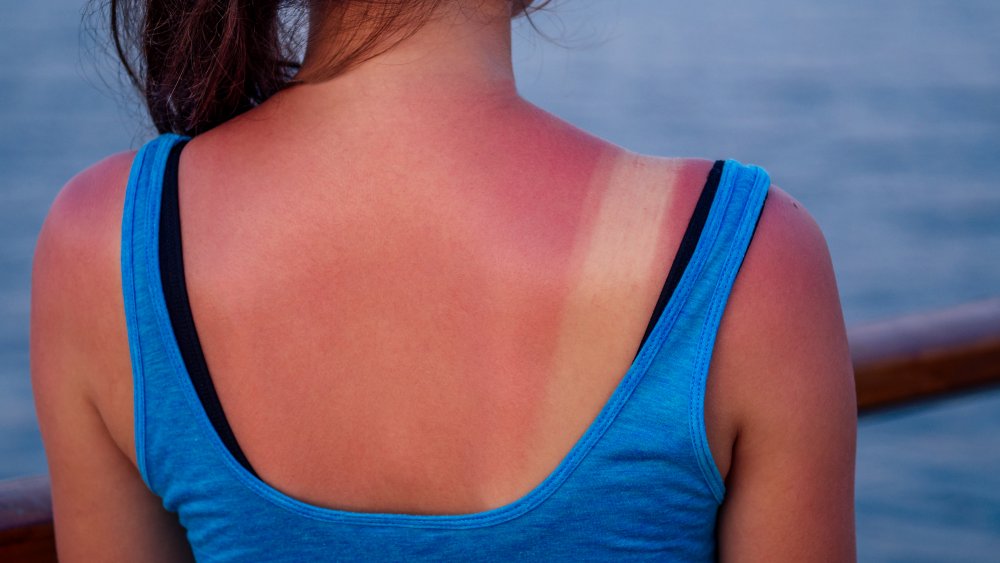
If you go tanning every day, you could get a nasty sunburn... even if you have a base tan
If you go tanning every day, you probably know that a base tan won't protect you from getting sunburned. In fact, tanning before hitting the beach only adds to your skin's sun damage, and it most certainly isn't an excuse to forgo sunscreen.
"You still need to protect yourself with sunscreen, reapply every two hours, and try to stay in the shade," dermatologist George W. Monks told Self. The doctor continued, explaining that these protective tips "hold true for anyone," no matter how dark your skin tone may be or how much melanin your skin may naturally have. Additionally, Miami-based dermatologist S. Manjula Jegasothy told InStyle that tanning with a base tan does "more harm than good, because even minimal amounts of UV radiation can cause sunburn cells." Added the doctor, "This leads to DNA damage in the skin cells, which in the long term, can lead to skin cancer."
In the end, it's best to use a sunless bronzer or tanner for a makeshift "base tan." However, don't forget to apply sunscreen before basking in the hot sun.
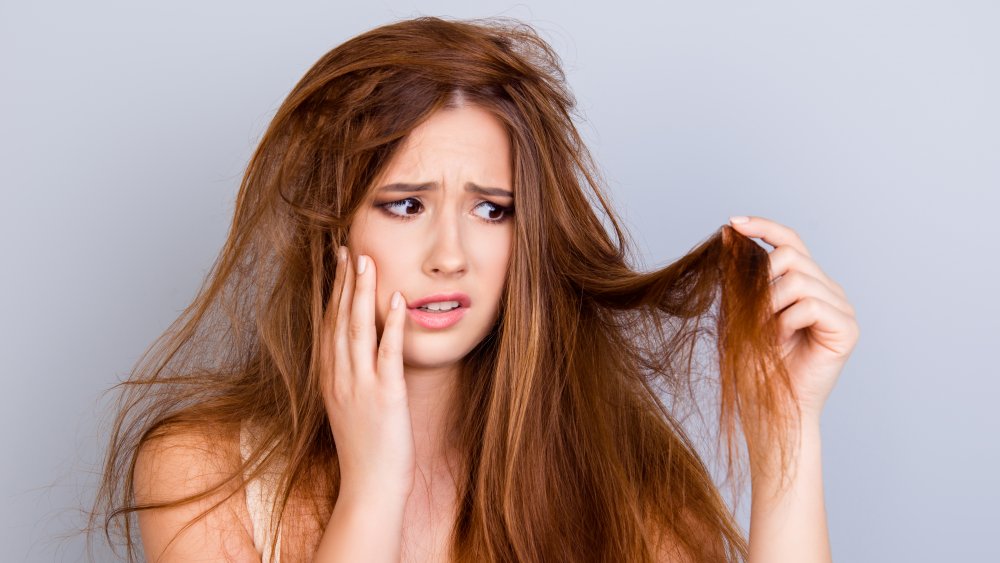
If you tan every day, your hair may feel dry and brittle
If you tan every day, you may want to indulge in a deep hair conditioning treatment. After all, the sun often sucks the moisture from your hair, likely leaving your locks craving a salon visit.
Just as your skin needs lotion after being in the sun all day, your hair needs some extra TLC, too. According to Dr. Doris Day, who spoke to Cosmopolitan about the havoc too much sun can wreak on your body, any natural moisture your hair may have had prior to tanning is typically sucked dry by the sun, leading to brittle locks or even breakage.
As noted by a study published in the Journal of Cosmetic Science, the remedy for sun-dried hair could be coconut oil, as the popular, convenient product found in most medicine cabinets has been proven to prevent protein loss in all types of hair — including undamaged, chemically treated, bleached, and UV ray exposed tresses (via Healthline). The truth about coconut oil is that it's better able to protect your strands thanks to its "low molecular weight and straight linear chain, [which make it] able to penetrate inside the hair shaft."
Tanning every day can alter your hair color
When you go tanning every day, you may be risking the vibrancy and hue of your hair color.
According to Real Simple, your natural hair color can become lighter when exposed to the sun, while color-treated hair may fade after spending too much time soaking up rays. While it may sound strange that UV rays can darken the skin while also turning hair blonde, Dr. Aaron Shafer from Stanford University can explain. According to Shafer, while your skin is made up of living cells, your hair is technically dead. As a result, your skin cells can respond to UV rays by producing melanin, while your hair is forced to "take the full brunt of the sun without any defenses."
NYC hair colorist Lauren Hack told Reader's Digest that it's incredibly important to "protect your color-treated tresses in the sun, chlorine, and salt water," unless, of course, you want a change in hair color. The same goes for indoor tanning, as the rays in a tanning booth are just as harmful (or perhaps even more damaging) than the natural rays to which you're exposed when you go outside (via The Miami Herald).