Surprising Things The Male Body Can Actually Do
Can we get real for a minute? Being a human is just downright weird sometimes — regardless of sex. Sure, we're pretty used to our own bodies, but that's not to say they don't do some strange things. Men's bodies, in particular, can go through some Twilight Zone-quality stuff. From being able to develop the ability to lactate — no joke — to experiencing Irritable Male Syndrome, a hormonal condition somewhat similar to PMS, there are tons of surprising things that can happen to those with the XY chromosome.
While these things certainly can occur, there are also plenty of freaky things that can — and do — happen to just about every biological male. Need proof? Here are some of the strangest and most surprising things that the average male body can actually do. We'll warn you though, you may never be able to look at the men in your life quite the same way again.
Transform from female to male in the womb
Arguably one of the strangest thing a male can do is, well, become a male. Biologically speaking, all males were once female. "Everyone comes from a common genetic and developmental framework that is tweaked by sex hormones," Richard Bribiescas, director of the Yale Reproductive Ecology Laboratory, told Men's Health.
Embryos have both male and female sex chromosomes, but it isn't until hormones develop that a distinction is made. Without testosterone, all embryos would be female. Say what, now? One of the easiest ways to prove this reality comes down to the nipples. Hear us out: have you ever wondered why men have nipples? Come on, we all have. According to Dr. Bribiescas, fetuses develop nipples very early on. But, due to testosterone, most men won't develop the ability to produce milk whereas women will. Yes, hormones are what render a man's nipples basically decorative.
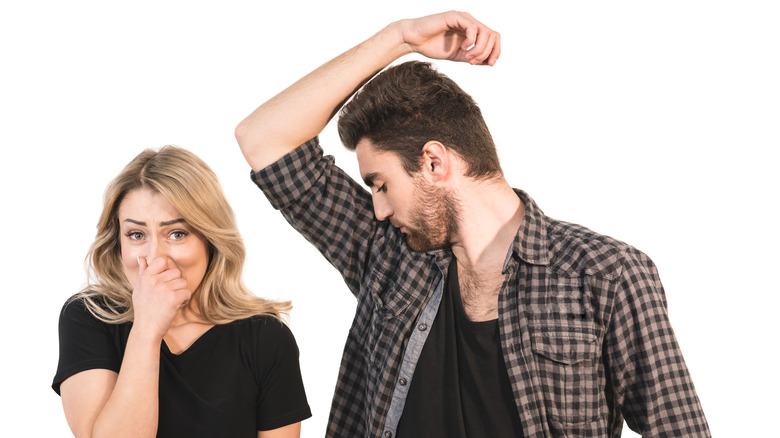
Produce an odd odor
Thanks to testosterone, men secrete androstenone — a steroidal pheromone — through both sweat and urine. This pheromone produced by the male body also happens to carry a strong odor — but how this odor is perceived can vary greatly.
According to a comprehensive study (via Scientific American) conducted by scientists at the Duke University Medical Center in North Carolina and The Rockefeller University in New York, three distinct reactions were noted. Around 62 percent of those who participated in the study found that the odor smelled like urine and thus, of course, was unpleasant. A much smaller percentage found the pheromone to have a sweet smell, similar to vanilla. Lastly, a third group of people couldn't smell anything — neither good nor bad.
If you're wondering how something could smell good to one person, bad to another, and like nothing at all to someone else, it all comes down to genetic variations. While men are responsible for producing androstenone, we're all involved in how the smell is perceived. Biology is strange.
This common male experience starts happening in the womb
After having a routine ultrasound to discover the sex of her baby, a woman took to the BabyCenter forums to get advice from other moms. According to the mother's account, the ultrasound technician and the sonogram itself revealed that the fetus was not only male, but was experiencing an erection. Could this be possible? As it turns out, yes. And it's really not all that uncommon.
"The phenomenon of fetal erection has been recognized for some two decades," wrote A.A. Jakobovits from the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Toldy Ference Hospital in Hungary. "Advanced technology has made it possible to demonstrate its occurrence even before the 16th week of gestation." Jakobovits went on to explain that he himself had observed the "phenomenon."
According to Los Angeles Times, some scientists think fetuses — as young as 12 weeks old — experience in-utero fetal penile erections as a way to keep penile tissue oxygenated, which is, apparently, good for it. The more you know.
The "semen-displacement hypothesis"
While we're on the topic of men's junk, why not delve into the totally bizarre — yet plausible — theory known as the "semen-displacement hypothesis"? According to the research by Gordon Gallup Jr., a psychologist at the University at Albany, and Rebecca Burch, an assistant professor of human development at Oswego State University, "the morphology of the human penis may act to plunge another male's ejaculate from the reproductive tract of his partner." Or, as BBC News put it: "[the] penis is a competitive beast."
Gallup told the publication that their hypothesis demonstrates that "the human penis may enable males to substitute their semen for the semen of their competitors." Although this idea has not yet been proven, the research and experiments provide the basis for the belief. Even urologist Derek Machin, who considers the theory "far fetched," thinks the research is more or less infallible. Or should we say, inphallible. Still, he says he is "not convinced that just because the penis does something like this it was necessarily designed to have that effect."
The speed of sperm
Sperm may be referred to as little swimmers, but they're actually more like Olympic swimmers... who jump off diving boards... while wearing jetpacks. Although you might assume it makes a difference when it comes to getting pregnant, semen expulsion speed doesn't actually have an effect — positive or negative — on impregnation. Yet and still, the average speed at which of these "swimmers" are expelled may surprise you.
According to Mark Elliot, director of the Institute for Psychological and Sexual Health in Columbus, Ohio, it's an incredible — wait for it — 28 miles per hour. To put that into perspective, that's faster than Usain Bolt, the world's fastest runner. It's also faster than the speed you're allowed to drive in many residential areas.
After their initial dive into the pool, so to speak, sperm slow down considerably. As Elliot told Men's Health, it takes nearly five minutes for sperm to reach the cervix and as many as three days to get to an egg.
A little testosterone goes a long way
Testosterone is a big deal. It's what's responsible for turning embryos biologically male, after all. If this hormone decreases, men can experience a whole host of changes to their bodies, including erectile dysfunction, weight gain, increased body fat, a lack of energy, difficulty concentrating, and even depression. You might reason, then, that men are just chock-full of it — especially men who are aggressive, violent, or both. However, science has proved that testosterone cannot be blamed for these attributes.
Testosterone is also not something that's just pumping through men's veins in high quantities. The normal range is anywhere between 270 to 1070 ng/dL (nanogram per deciliter of blood) — though researchers feel that the healthiest men have levels around 400 to 600 ng/dL. But, what does that even mean? Both nanograms and deciliters are very, very small units of measure. Men's Health explained that if you were able to gather all of the testosterone from an average man's body, "it would barely fog the bottom of a shot glass." Still, it's an important hormone.
They go through a menopause of sorts
Although menopause is a widely-known phenomenon that affects women, "male menopause" — or andropause — is indeed a thing as well, and it affects men who are aged 50 and older. That said, it is markedly different than menopause. As many women know, menopause is the result of changes in the amount of hormones produced. Men, on the other hand, don't actually stop producing hormones. However, many men will experience lower testosterone production in old age. Just as low testosterone in any age can cause symptoms like depression, low levels of testosterone in middle-aged and older men is much the same. The Cleveland Clinic reported fatigue, weakness, and impotence to be markers of "male menopause."
For men struggling with the symptoms of andropause, hormone replacement therapy may be a viable option to consider. Sadly, though, replacing lost testosterone can cause issues on its own — including worsening prostate cancer (if you have it) and increasing hardening of the arteries.
Outfart the ladies
If you're in a relationship with a man, you probably don't need science to tell that, yes, men do indeed fart more than women. Nevertheless, that is what science tells us. The exact reason for this is, however, is unknown. Marc Taormina, a gastroenterologist at Midwest Gastroenterology in Missouri, revealed to Semicolon Stories that there could be a number of components involved. "It could be diet, bigger GI tracts, and/or swallowing more air," he hypothesized. That's right, if men pass gas more due to having larger gastrointestinal tracts, then there could actually be a biological reason behind men's flatulence frequency.
Though, there could still be other factors at play. Aziz Aadam, assistant professor of medicine at Rush University Medical Center in Illinois, told Women's Health that men may fart more than women because they tend to eat faster and are generally less likely to be embarrassed by the bodily process. But, before you go tooting your own horn and walking around like your s*** don't stink, you should know that women's farts smell worse than men's. Sigh.